Local Dialects or Mother Tongues | Indian Culture
The languages of India primarily belong to two major linguistic families, Indo-European (whose branch Indo-Aryan is spoken by about 75 percent of the population) and Dravidian (spoken by about 25 percent). Other languages spoken in India come mainly from the Austro-Asiatic and Tibeto-Burman linguistic families, as well as a few language isolates. Individual mother tongues in India number several hundred and more than a thousand if major dialects are included. While Hindi is the official language of the central government in India, with English as a provisional official sub-language, individual state legislatures can adopt any regional language as the official language of that state. The Constitution of India recognizes 23 official languages, spoken in different parts of the country, and two official classical languages, Sanskrit and Tamil.
The census enumerators were asked to write down the names given by the individuals without making any correction. These mother tongues were then sought to be “rationalized” and identified with the languages or dialects through a careful analysis of the names. Sometimes the individuals gave the name of their caste as their language, not distinguishing between language and caste. Sometimes they gave the name of a language which they did not speak, but which is supposed to be used by the members of the religious group they belonged to. Sometimes, they gave the names of their profession. The region they came from was also used to indicate their speech. While such mixing of the names of languages with caste, profession, religion, and region, etc. somewhat led to a confusing picture of the actual languages spoken in the country, the process of rationalization often (not always) resulted in the identification of the language or dialect that the individual actually spoke. The names of the mother tongues listed in the Cenus of India 1961 clearly reveal the interesting pscho-social and political dynamics of language use in India. The very same dynamics are still in operation, although the subsequent Census reports on Indian languages somewhat tried to standardize the names, and not present the names of mother tongues as they were given by the people.
Abstract of Mother Tongues | Indian Languages
The Language Tables published by the Census of India 1961 is an important milestone in the study of Indian linguistic demography. The Census of India 1961 identified 1652 “mother tongues.” “Mother tongues” thus identified may not have been identical to the languages, dialects, or even speech forms of the individuals. These were the labels used by the individuals to identify their speech, when asked to give the name of the early childhood language used in the household of the individual. A total of 1652 mother tongue names were identified, but it should be remembered that mother tongues are not identical to languages or dialects. The question as to how many languages are spoken in India is still a question that cannot be answered with certainty. We really need another Linguistic Survey of India that will focus not only on identifying the languages and dialects of India, but will provide the unwritten languages with relevant script systems, prepare monolingual, bilingual, and multilingual dictionaries in the lesser known languages, provide resources for the use of these languages at least up to the elementary level in education, and describe and explain the dynamics of language use and identity in the country. A progressive and democratic nation should always feel proud of its diversity and the strength that it derives from such diversity.
The Constitution of India now recognizes 23 languages, spoken in different parts of the country. These consist of English plus 22 Indian languages: Assamese, Bengali, Bodo, Dogri, Gujarati, Hindi, Kannada, Kashmiri, Konkani, Maithili, Malayalam, Meitei, Marathi, Nepali, Oriya, Punjabi, Sanskrit, Santhali, Sindhi, Tamil, Telugu and Urdu. Hindi is a official language of the states of Uttar Pradesh, Bihar, Jharkhand, Uttaranchal, Madhya Pradesh, Rajasthan, Chattisgarh, Himachal Pradesh, Haryana and the National Capital Territory of Delhi. Tamil is an official language of Tamil Nadu, Puducherry and Andamon Nicobar Islands. English is the co-official language of the Indian Union, and each of the several states mentioned above may also have another co-official language.
The following table lists the 22 Indian languages set out in the eighth schedule as of May 2007, together with the regions where they are used:
S. No. | Indian Languages | Indian State(s)/Place(s)/Communities |
1. | Assamese/Asomiya | Assam |
2. | Bengali/Bangla | Andaman & Nicobar Islands, Tripura, West Bengal, |
3. | Bodo | Assam |
4. | Dogri | Jammu and Kashmir |
5. | Gujarati | Dadra and Nagar Haveli, Daman and Diu, Gujarat |
6. | Hindi | Andaman and Nicobar Islands, Arunachal Pradesh, Bihar, Chandigarh, Chhattisgarh, the national capital territory of Delhi, Haryana, Himachal Pradesh, Jharkhand, Madhya Pradesh, Rajasthan, Uttar Pradesh and Uttarakhand. |
7. | Kannada | Karnataka |
8. | Kashmiri | Jammu and Kashmir |
9. | Konkani | Goa, Karnataka, |
10. | Maithili | Bihar |
11. | Malayalam | Kerala, Andaman and Nicobar Islands, Lakshadweep |
12. | Manipuri (also Meitei or Meithei) | Manipur |
13. | Marathi | Dadra & Nagar Haveli, Daman and Diu, Goa, Maharashtra |
14. | Nepali | Sikkim, West Bengal |
15. | Oriya | Orissa |
16. | Punjabi | Chandigarh, Delhi, Haryana, Punjab |
17. | Sanskrit | Listed as a Classical Language of India. |
18. | Santhali | Santhal tribals of the Chota Nagpur Plateau (comprising the states of Bihar, Chattisgarh, Jharkhand, Orissa) |
19. | Sindhi | Sindhi community |
20. | Tamil | Tamil Nadu, Andaman & Nicobar Islands, Kerala, Puducherry . Listed as a Classical Language of India. |
21. | Telugu | Andaman & Nicobar Islands, Andhra Pradesh |
22. | Urdu | Andhra Pradesh, Delhi, Jammu and Kashmir, Uttar Pradesh, Tamil Nadu |
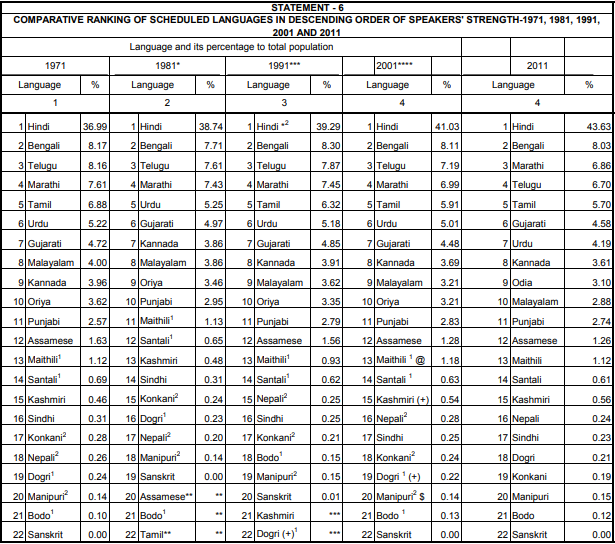
A comparative ranking of Indian Scheduled Languages | 1971 | 1981 | 1991 | 2001 | 2011
Mother Tongues | Indian Language Groups
As per the 2011 census, 43.63 percent of Indians speak Hindi as their mother tongue. Bengali, with 8.03 percent speakers, is second in the list, followed by Marathi at 3rd with 6.86 percent speakers, Telugu at 4th with 6.7 percent speakers and Tamil at 5th with 5.7 percent speakers. In all, 13 of the 22 scheduled languages were reported as the mother tongue by at least 1 percent of the population. Except for Sanskrit, each of the 21 scheduled languages was reported as the mother tongue by at least 10 lakh people. Sanskrit is the only language that is spoken by a set of around 25000 people.
Rise in Hindi language speakers : Hindi is the most spoken Indian language. It is one of two languages used by the Union government, the other being English. Currently, 43.63 percent of India speaks Hindi including languages such as Bhojpuri that are fighting to be accorded separate status. Between 2001 and 2011, Hindi grew at a rate of 25 percent, adding about 100 million new Hindi speakers. Among the 10 largest languages in India, Hindi is the only one that saw the rise in the proportion of its speakers. The language has been witnessing the growth since 1971, driven mostly by high population growth in the Hindi-speaking states.
Decline in South Indian language speakers : The lower population growth in the five Dravidian language-speaking states, namely Tamil Nadu, Karnataka, Kerala, Andhra Pradesh and Telangana has resulted in the fall in proportion of Telugu, Tamil, Kannada and Malayalam language speakers. While Hindi grew by 161 percent between 1971 and 2011, these four largest Dravidian languages grew at half that rate that is at 81 percent over the same period.
Growth of Hindi language speakers in South India : The growing movement of people from north to south has led to greater presence of Hindi in the five southern states. In Tamil Nadu, the proportion of Hindi speakers nearly doubled from 2001 to 2011. However, in some cases, this growing migration from North to South resulted in agitation such as in Bengaluru, Karnataka; the government was forced to remove Hindi signages from the city metro.
Drop in numbers of Urdu speakers : As per the language census data 2011, two scheduled languages, Urdu and Konkani, saw fall in absolute numbers. There are 50772631 Urdu speakers in India, a fall of about 1.5 percent since 2001. The decline in Konkani speakers is 9.5 percent. Urdu speakers are spread across India but the language’s strongest presence is in the two largest Urdu-speaking states – Uttar Pradesh and Bihar. The Urdu language in modern India is associated only with Muslims, however, this fall in Urdu speakers is strange as the Muslim population in Uttar Pradesh and Bihar has grown between 2001 and 2011.
Bengali retains its position as 2nd most spoken language : As per the 2011 census, Bengali, with 8.03 percent, is second in the list after Hindi in terms of percentage of speakers. As Hindi language, Bengali too spreads to other states with migration. The language is spreading to the south and west, there are 4.4 lakh Bengalis in far-off Maharashtra and 2.2 lakh in Delhi. In South, the numbers are small, however, they are growing. In Kerala, the proportion of Bengali speakers has grown nine times.
Sharpest language divides in Assam : The sharpest language divide of India exists in Assam, where a proposed citizenship law and National Register of Citizens have divided the state’s Assamese and Bengali speakers. Assam is the only major state that does not have any language group in a majority. Assamese speakers, the largest group, make up 48 percent of the state, however, the proportion of Bengali speakers went up in 2001-2011.
Increase in English language speakers : English seems to have registered a 15 percent jump in number of speakers since 2001, making it one of the fastest growing languages in the decade.
Decline in tribal languages speakers : The lesser-known tribal languages spoken in remote corners of India have shown a decline, as per the findings of the 2011 Language Census. These include the Sema language of the Naga tribe, the Monpa language of Arunachal Pradesh, Nagaland’s Phom, Odisha’s Jatapu, Himachal Pradesh’s Lahauli and Bhumij of Eastern India
Language Census
- The primary objective of the Linguistic Survey of India is to present an updated linguistic scenario.
- The census followed a certain methodology to arrive at these findings. It defined “Mother tongue” as ‘the language spoken in childhood by the person’s mother to the person. If the mother died in infancy, the language mainly spoken in the person’s home in childhood will be the mother tongue’.
- There are total 121 languages that are considered as mother tongues. Of these, 22 languages are included in the Eighth Schedule of the Indian Constitution.
- The 22 languages included in the Eighth Schedule account for the mother tongue of 96.72 percent Indians as per the 2011 census.
The following table lists the names of Mother Tongues and their respective language groups. Kindly inform us, if any local dialects missed under these Indian language groups.
S. No. | Mother Tongue Names | Total Speakers | Language Groups |
1 | Assamese | 14816414 | ASSAMESE |
2 | Bengali | 96177835 | BENGALI |
3 | Chakma | 228281 | BENGALI |
4 | Haijong/Hajong | 71792 | BENGALI |
5 | Rajbangsi | 475861 | BENGALI |
6 | Bodo/Boro | 1454547 | BODO |
7 | Kachari | 15984 | BODO |
8 | Mech/Mechhia | 11546 | BODO |
9 | Dogri | 2596763 | DOGRI |
10 | Gujarati | 55036204 | GUJARATI |
11 | Gujrao/Gujrau | 15431 | GUJARATI |
12 | Pattani | 16510 | GUJARATI |
13 | Ponchi | 13812 | GUJARATI |
14 | Saurashtra/Saurashtri | 247702 | GUJARATI |
15 | Awadhi | 3850906 | HINDI |
16 | Baghati/Baghati Pahari | 15835 | HINDI |
17 | Bagheli/Baghel Khandi | 2679129 | HINDI |
18 | Bagri Rajasthani | 234227 | HINDI |
19 | Banjari | 1581271 | HINDI |
20 | Bhadrawahi | 98806 | HINDI |
21 | Bhagoria | 20924 | HINDI |
22 | Bharmauri/Gaddi | 181069 | HINDI |
23 | Bhojpuri | 50579447 | HINDI |
24 | Bishnoi | 12079 | HINDI |
25 | Brajbhasha | 1556314 | HINDI |
26 | Bundeli/Bundel khandi | 5626356 | HINDI |
27 | Chambeali/Chamrali | 125746 | HINDI |
28 | Chhattisgarhi | 16245190 | HINDI |
29 | Churahi | 75552 | HINDI |
30 | Dhundhari | 1476446 | HINDI |
31 | Garhwali | 2482089 | HINDI |
32 | Gawari | 19062 | HINDI |
33 | Gojri/Gujjari/Gujar | 1227901 | HINDI |
34 | Handuri | 47803 | HINDI |
35 | Hara/Harauti | 2944356 | HINDI |
36 | Haryanvi | 9806519 | HINDI |
37 | Hindi | 322230097 | HINDI |
38 | Jaunpuri/Jaunsari | 136779 | HINDI |
39 | Kangri | 1117342 | HINDI |
40 | Khari Boli | 50195 | HINDI |
41 | Khortha/Khotta | 8038735 | HINDI |
42 | Kulvi | 196295 | HINDI |
43 | Kumauni | 2081057 | HINDI |
44 | Kurmali Thar | 311175 | HINDI |
45 | Lamani/Lambadi | 3276548 | HINDI |
46 | Laria | 89876 | HINDI |
47 | Lodhi | 139180 | HINDI |
48 | Magadhi/Magahi | 12706825 | HINDI |
49 | Malvi | 5212617 | HINDI |
50 | Mandeali | 622590 | HINDI |
51 | Marwari | 7831749 | HINDI |
52 | Mewari | 4212262 | HINDI |
53 | Mewati | 856643 | HINDI |
54 | Nagpuria | 763014 | HINDI |
55 | Nimadi | 2309265 | HINDI |
56 | Padari | 17279 | HINDI |
57 | Pahari | 3253889 | HINDI |
58 | Palmuha | 23579 | HINDI |
59 | Panch Pargania | 244914 | HINDI |
60 | Pando/Pandwani | 15595 | HINDI |
61 | Pangwali | 18668 | HINDI |
62 | Pawari/Powari | 325772 | HINDI |
63 | Puran/Puran Bhasha | 12375 | HINDI |
64 | Rajasthani | 25806344 | HINDI |
65 | Sadan/Sadri | 4345677 | HINDI |
66 | Sirmauri | 107401 | HINDI |
67 | Sondwari | 229788 | HINDI |
68 | Sugali | 170987 | HINDI |
69 | Surgujia | 1738256 | HINDI |
70 | Surjapuri | 2256228 | HINDI |
71 | Badaga | 133550 | KANNADA |
72 | Kannada | 43506272 | KANNADA |
73 | Kuruba/Kurumba | 24189 | KANNADA |
74 | Prakritha/Prakritha Bhasha | 12257 | KANNADA |
75 | Kashmiri | 6554369 | KASHMIRI |
76 | Kishtwari | 39748 | KASHMIRI |
77 | Siraji | 124896 | KASHMIRI |
78 | Dardi | 25600 | KASHMIRI |
79 | Konkani | 2146906 | KONKANI |
80 | Kudubi/Kudumbi | 17209 | KONKANI |
81 | Malwani | 23617 | KONKANI |
82 | Nawait | 13123 | KONKANI |
83 | Gorboli/Goru/Gorwani | 50259 | KONKANI |
84 | Maithili | 13353347 | MAITHILI |
85 | Purbi Maithili | 11116 | MAITHILI |
86 | Thati | 165420 | MAITHILI |
87 | Tharu | 53575 | MAITHILI |
88 | Malayalam | 34776533 | MALAYALAM |
89 | Pania | 22808 | MALAYALAM |
90 | Yerava | 26563 | MALAYALAM |
91 | Manipuri | 1760913 | MANIPURI |
92 | Are | 53879 | MARATHI |
93 | Koli | 13809 | MARATHI |
94 | Marathi | 82801140 | MARATHI |
95 | Nepali | 2925796 | ODIA |
96 | Bhatri | 334258 | ODIA |
97 | Bhuiya/Bhuyan[Ori] | 32126 | ODIA |
98 | Bhumijali | 34651 | ODIA |
99 | Desia | 227313 | ODIA |
100 | Odia | 34059266 | ODIA |
101 | Proja (Ori) | 156354 | ODIA |
102 | Relli | 12969 | ODIA |
103 | Sambalpuri | 2630381 | ODIA |
104 | Bagri | 1656588 | PUNJABI |
105 | Bhateali | 23970 | PUNJABI |
106 | Bilaspuri Kahluri | 295805 | PUNJABI |
107 | Punjabi | 31144095 | PUNJABI |
108 | Sanskrit | 24709 | SANSKRIT |
109 | Karmali | 358579 | SANTALI |
110 | Mahili | 26399 | SANTALI |
111 | Santali | 6973345 | SANTALI |
112 | Bhatia | 22409 | SINDHI |
113 | Kachchhi | 1030602 | SINDHI |
114 | Sindhi | 1679246 | SINDHI |
115 | Irula/Irular Mozhi | 11870 | TAMIL |
116 | Kaikadi | 25870 | TAMIL |
117 | Korava | 10421 | TAMIL |
118 | Tamil | 68888839 | TAMIL |
119 | Yerukala/Yerukula | 58065 | TAMIL |
120 | Telugu | 80912459 | TELUGU |
121 | Vadari | 198020 | TELUGU |
122 | Urdu | 50725762 | URDU |
123 | Bhansari | 22806 | URDU |
124 | Adi | 110307 | ADI |
125 | Adi Gallong/Gallong | 29246 | ADI |
126 | Adi Miniyong/Miniyong | 13344 | ADI |
127 | Talgalo | 69256 | ADI |
128 | Afghani/Kabuli/Pashto | 21433 | AFGHANI/KABULI/PASHTO |
129 | Anal | 24301 | ANAL |
130 | Angami | 40721 | ANGAMI |
131 | Ao | 119549 | AO |
132 | Chungli | 70782 | AO |
133 | Mongsen | 69094 | AO |
134 | Arabic/Arbi | 54871 | ARABIC/ARBI |
135 | Balti | 13654 | BALTI |
136 | Baori | 63028 | BHILI/BHILODI |
137 | Barel | 991257 | BHILI/BHILODI |
138 | Bhilali | 753466 | BHILI/BHILODI |
139 | Bhili/Bhilodi | 3206533 | BHILI/BHILODI |
140 | Chodhari | 110570 | BHILI/BHILODI |
141 | Dhodia | 49097 | BHILI/BHILODI |
142 | Gamti/Gavit | 139118 | BHILI/BHILODI |
143 | Garasia | 76749 | BHILI/BHILODI |
144 | Kokna/Kokni/Kukna | 416787 | BHILI/BHILODI |
145 | Mawchi | 98486 | BHILI/BHILODI |
146 | Paradhi | 69085 | BHILI/BHILODI |
147 | Pawri | 311677 | BHILI/BHILODI |
148 | Rathi | 47801 | BHILI/BHILODI |
149 | Tadavi | 52347 | BHILI/BHILODI |
150 | Varli | 387481 | BHILI/BHILODI |
151 | Vasava | 187036 | BHILI/BHILODI |
152 | Wagdi | 3393991 | BHILI/BHILODI |
153 | Bhotia | 120583 | BHOTIA |
154 | Bauti | 100000 | BHOTIA |
155 | Bhumij | 10190 | BHUMIJ |
156 | Bishnupriya Manipuri/Manipuri Bishnupriya | 74069 | BISHNUPURIYA |
157 | Chakhesang | 19846 | CHAKHESANG |
158 | Chakru/Chokri | 91216 | CHAKRU/CHOKRI |
159 | Chang | 66852 | CHANG |
160 | Coorgi/Kodagu | 16939 | COORGI/KODAGU |
161 | Kodava | 96918 | COORGI/KODAGU |
162 | Deori | 32376 | DEORI |
163 | Dimasa | 133327 | DIMASA |
164 | English | 259678 | ENGLISH |
165 | Gadaba | 40965 | GADABA |
166 | Gangte | 16542 | GANGTE |
167 | Garo | 1125359 | GARO |
168 | Dorli | 47701 | GONDI |
169 | Gondi | 2856581 | GONDI |
170 | Kalari | 26769 | GONDI |
171 | Maria/ Muria | 15864 | GONDI |
172 | Halabi | 765464 | HALABI |
173 | Halam | 26534 | HALAM |
174 | Hmar | 98988 | HMAR |
175 | Ho | 1410996 | HO |
176 | Lohara | 10422 | HO |
177 | Jatapu | 19990 | JATAPU |
178 | Juang | 30378 | JUANG |
179 | Kabui | 54220 | KABUI |
180 | Rongmei | 68706 | KABUI |
181 | Karbi/Mikir | 528503 | KARBI/MIKIR |
182 | Ahirani | 1636465 | KHANDESHI |
183 | Dangi | 150674 | KHANDESHI |
184 | Gujari | 57171 | KHANDESHI |
185 | Khandeshi | 10670 | KHANDESHI |
186 | Kharia | 293665 | KHARIA |
187 | Khasi | 1037964 | KHASI |
188 | Lyngngam | 11586 | KHASI |
189 | Pnar/Synteng | 319324 | KHASI |
190 | War | 51558 | KHASI |
191 | Khezha | 36383 | KHEZHA |
192 | Khiemnungan | 61968 | KHIEMNUNGAN |
193 | Khond/Kondh | 111693 | KHOND/KONDH |
194 | Kuvi | 43855 | KHOND/KONDH |
195 | Kinnauri | 83427 | KINNAURI |
196 | Kisan | 206100 | KISAN |
197 | Koch | 33962 | KOCH |
198 | Koda/Kora | 47181 | KODA/KORA |
199 | Kolami | 128451 | KOLAMI |
200 | Kom | 15108 | KOM |
201 | Kodu | 32166 | KONDA |
202 | Konda | 24987 | KONDA |
203 | Konyak | 244477 | KONYAK |
204 | Korku | 688053 | KORKU |
205 | Muwasi | 35827 | KORKU |
206 | Koraku | 16154 | KORWA |
207 | Koya | 407423 | KOYA |
208 | Kui | 941377 | KUI |
209 | Kuki | 82049 | KUKI |
210 | Kurukh/Oraon | 1976920 | KURUKH/ORAON |
211 | Ladakhi | 14952 | LADAKHI |
212 | Lahauli | 11162 | LAHAULI |
213 | Bahawal Puri | 29253 | LAHNDA |
214 | Hindi Multani | 61722 | LAHNDA |
215 | Mara | 38671 | LAKHER |
216 | Lalung | 33921 | LALUNG |
217 | Lepcha | 47331 | LEPCHA |
218 | Liangmei | 48388 | LIANGMEI |
219 | Limbu | 38067 | LIMBU |
220 | Lotha | 179467 | LOTHA |
221 | Lushai/Mizo | 825900 | LUSHAI/MIZO |
222 | Pahariya | 152814 | MALTO |
223 | Kulehiya | 75776 | MALTO |
224 | Mao | 97195 | MAO |
225 | Paola | 143001 | MAO |
226 | Maram | 32460 | MARAM |
227 | Maring | 25814 | MARING |
228 | Miri/Mishing | 629954 | MIRI/MISHING |
229 | Mishmi | 15871 | MISHMI |
230 | Mogh | 36652 | MOGH |
231 | Monpa | 13703 | MONPA |
232 | Kol | 19868 | MONPA |
233 | Munda | 464817 | MUNDA |
234 | Mundari | 1128050 | MUNDARI |
235 | Nicobarese | 29099 | NICOBARESE |
236 | Apatani | 44815 | NISSI/DAFLA |
237 | Nissi/Dafla | 289166 | NISSI/DAFLA |
238 | Tagin | 62897 | NISSI/DAFLA |
239 | Nocte | 29810 | NOCTE |
240 | Paite | 79443 | PAITE |
241 | Dhurwa | 45938 | PARJI |
242 | Pawi | 28639 | PAWI |
243 | Phom | 54416 | PHOM |
244 | Pochury | 21568 | POCHURY |
245 | Rabha | 139985 | RABHA |
246 | Rai | 10427 | RAI |
247 | Rengma | 65328 | RENGMA |
248 | Sangtam | 75684 | SANGTAM |
249 | Savara | 409481 | SAVARA |
250 | Sema | 10802 | SEMA |
251 | Sherpa | 16012 | SHERPA |
252 | Shina | 32069 | SHINA |
253 | Tamang | 20154 | TAMANG |
254 | Tangkhul | 187263 | TANGKHUL |
255 | Tutcha Tangsa | 10234 | TANGSA |
256 | Thado | 227114 | THADO |
257 | Tibetan | 83779 | TIBETAN |
258 | Purkhi | 93500 | TIBETAN |
259 | Kokbarak | 917900 | TRIPURI |
260 | Reang | 58539 | TRIPURI |
261 | Tripuri | 33138 | TRIPURI |
262 | Tulu | 1841963 | TULU |
263 | Vaiphei | 42748 | VAIPHEI |
264 | Wancho | 59154 | WANCHO |
265 | Chirr | 12300 | YIMCHUNGRE |
266 | Tikhir | 11071 | YIMCHUNGRE |
267 | Yimchungre | 56538 | YIMCHUNGRE |
268 | Zeliang | 63529 | ZELIANG |
269 | Zemi | 50923 | ZEMI |
270 | Zou | 26545 | ZOU |
Wherever English has spread in the last 200 years, local languages have been wiped out. Over 100 aboriginal languages in Australia have disappeared in the last two centuries. Similar stories abound in the Indian Subcontinent. The 1961 census records India as having 1,652 languages. By 1971, it was 808. Over 220 Indian languages have been lost in the last 50 years, with a further 197 languages categorized as endangered according to the People’s Linguistic Survey of India, 2013. Somehow, despite our faith in diversity, we simply are not able to quantify it, especially in terms of languages and dialects. Out of the 197 endangered languages, only Boro and Meithei have official status in India, as they have a writing system. Such an Act forgets that most of our great scriptures and epics are part of an oral tradition, embossed into actual writing over centuries. Such methodologies should be reformed, granting greater recognition to oral traditions in different languages. If possible on their hands, everybody should works on protection, preservation and documentation of all the mother tongues/languages of India spoken by millions of people which are called endangered languages.
EXPLORE THE ECSTATIC VIGOUR OF PROSPEROUS CULTURES
Alluring Melody of Cultures, Traditions, Rituals, Structures and Legislations.